Virtual Address
support@digiq.blog
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) is a standardized notation for modeling business processes. This standard allows the creation of process models in any system that uses BPMN notation. The various objects within the models simplify the understanding of processes, even for those unfamiliar with BPMN. This article aims to provide a brief introduction to BPMN, highlighting the basic elements of the processes. While BPMN includes many more elements than those discussed here, this overview will introduce you to the most essential components if you are new to BPMN.
Structured processes, meaning processes that can easily predict the next steps, are best suited for modeling. It is also possible to model partially structured processes, but this is much more complex.
The most important elements of BPMN are:
Activities:
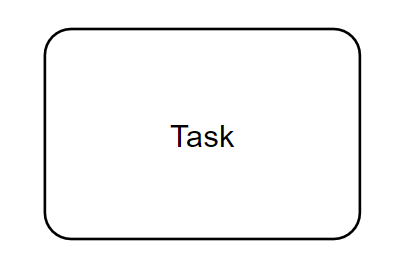
Activities describe actions that occur during a process. These activities are displayed as rectangles. They are usually labeled using a “verb + noun” phrase, such as “contact reception” or “print document”. This convention helps to keep the process understandable and standardized.
In the real business world, it is not always possible to strictly keep to this convention, but following this structure as closely as possible helps to ensure clarity.
Events:

Events describe a state in BPMN. Processes always begin and end with an event in BPMN. These events are referred to as start and end events. Start events are shown as circles with a thin border, while end events are shown as circles with a thick border. They describe a state before and after the process.
There are also intermediate events in BPMN. These events describe a state that occurs during the process. These intermediate events make it possible to react to certain conditions or events without restarting or interrupting the entire process.
Gateways:
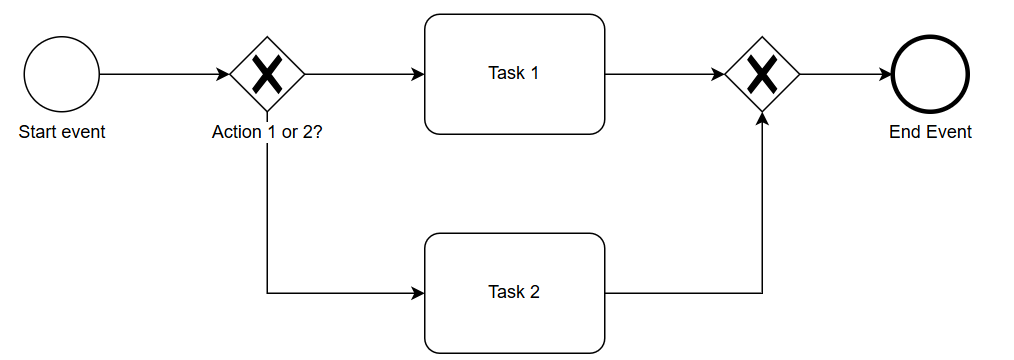
Gateways in BPMN control the flow of a process. They are used to separate or merge the flow at decision points. Gateways help define different paths in the process based on conditions or events. Usually, BPMN Gateways also close with the same Gateways after the different actions have been completed, as shown in the example below. But in some cases, it is not possible to close the gateway.
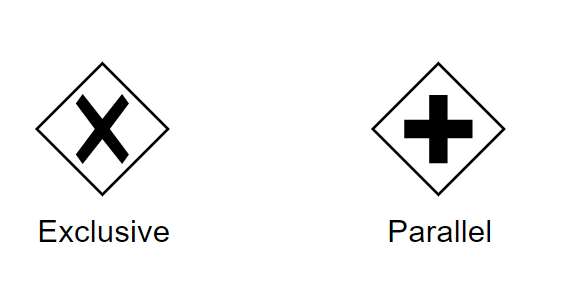
Exclusive gateways are used to make decisions in the process flow. They split the process into different paths based on specific conditions or decisions. Only one path is followed, meaning the process flow is restricted to a single option. This is important when different conditions necessitate different actions.
Parallel gateways are used to run activities in the process at the same time. They split the process flow into several parallel paths that are carried out together, and then bring these paths back together once all tasks are done. This is useful when multiple tasks need to be done separately and at the same time.
Pools/Lanes:

Pools represent independent units or organizations that are involved in the process. A pool typically represents an entire organization. Pools delineate the area of responsibility of a specific organizational unit and are particularly useful for visualizing the interactions between different organizations or entities.
Lanes are subdivisions within a pool that represent specific roles, departments, or individuals within the organization. Using lanes makes it easier to assign tasks and responsibilities and clearly shows who is responsible for which activities in the process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BPMN 2.0 offers a comprehensive and standardized way to model business processes, making them accessible even to those unfamiliar with the notation. By utilizing essential elements like activities, events, gateways, and pools/lanes, BPMN ensures that processes are clearly defined and easily understood. While this article provided a brief overview of these fundamental components, it is important to recognize that BPMN encompasses a broader range of elements that cater to more complex scenarios. Properly leveraging BPMN can significantly enhance the clarity and efficiency of business process management, especially for structured and partially structured processes.